Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). It occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it does produce. There are three primary types: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells. Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, often results from lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth but may increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Early detection of diabetes can help prevent complications. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing wounds. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and testing.
While Type 1 diabetes symptoms may appear suddenly, Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop gradually. Some people may have prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. Regular check-ups and screenings can help catch diabetes early and allow for better management.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes Control
A well-balanced diet is essential for managing diabetes effectively. The focus should be on nutrient-dense foods that help regulate blood sugar levels.
Eating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods can support stable glucose levels. Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-glycemic-index carbohydrates that cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. Portion control is equally important, as consuming large meals can lead to blood sugar fluctuations.
Meal planning and mindful eating habits can make a significant difference. Incorporate plenty of vegetables, fruits in moderation, and sources of protein such as fish, tofu, or legumes. Drinking enough water and limiting alcohol and sugary beverages also help maintain stable glucose levels.
The Importance of Physical Activity
Regular exercise is a key component of diabetes management. Physical activity helps the body use insulin more effectively, reduces blood sugar levels, and promotes overall well-being.
Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week can improve insulin sensitivity. Strength training exercises like weightlifting or resistance band workouts also help build muscle mass and regulate blood sugar levels.
For individuals with diabetes, it’s essential to monitor blood sugar before and after exercise. Carrying a small snack or glucose tablets can help manage sudden drops in blood sugar, especially for those on insulin therapy.
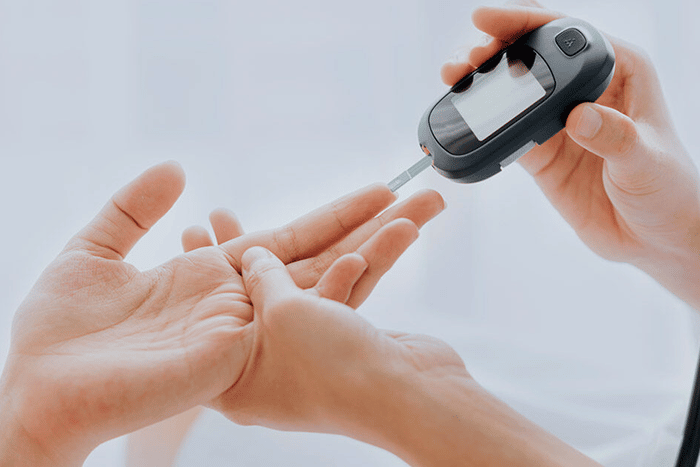
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Tracking blood sugar levels regularly is a fundamental aspect of diabetes care. Monitoring helps individuals understand how food, exercise, medication, and stress impact glucose levels.
Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system provides real-time data on blood sugar fluctuations. Keeping a log of readings and trends allows individuals and healthcare providers to make necessary adjustments in diet, activity levels, or medications.
Target blood sugar levels may vary for each person, but general guidelines suggest maintaining fasting blood sugar between 80 and 130 mg/dL and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dL. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider ensure proper management and prevent complications.
Managing Stress and Mental Health

Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels by triggering the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which increases glucose production. Managing stress effectively is crucial for diabetes control.
Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, can help reduce stress and improve emotional well-being. Engaging in hobbies, socializing, and maintaining a positive mindset contribute to a balanced and healthier lifestyle.
If stress or emotional challenges become overwhelming, seeking support from a therapist or counselor specializing in chronic health conditions can provide valuable coping strategies.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be enough to manage diabetes, and medications or insulin therapy become necessary. Healthcare providers may prescribe oral medications to help regulate blood sugar levels, while insulin therapy is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and some with Type 2 diabetes.
Different types of insulin include rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting, each serving a specific purpose in blood sugar control. Understanding medication schedules, dosages, and proper injection techniques ensures optimal effectiveness.
Always follow the prescribed treatment plan, and communicate with healthcare professionals about any side effects or concerns regarding medications.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Long-term complications of diabetes can include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage (neuropathy), eye problems (retinopathy), and foot ulcers. Preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of these complications.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and scheduling regular medical check-ups are essential steps. Proper foot care, including daily inspections for cuts or sores and wearing comfortable footwear, can prevent diabetic foot complications.
Additionally, staying up-to-date with vaccinations, such as flu shots and pneumonia vaccines, helps protect against infections that may be harder to manage with diabetes.
The Role of Support Systems
Having a strong support system makes diabetes management easier. Family, friends, and support groups provide emotional encouragement, motivation, and practical advice for living with diabetes.
Connecting with diabetes communities through online forums, local support groups, or diabetes education programs allows individuals to share experiences, exchange tips, and stay informed about the latest advancements in diabetes care.
Final Thoughts
Managing diabetes requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating a healthy diet, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, stress management, and medication adherence. With proper strategies and lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
By staying proactive, making informed choices, and seeking medical guidance, diabetes can be effectively controlled, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing overall well-being. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.