Cancer of the male reproductive system, particularly the testicles, is relatively rare compared to other forms of cancer, but it’s essential to be aware of its signs, symptoms, and risk factors.
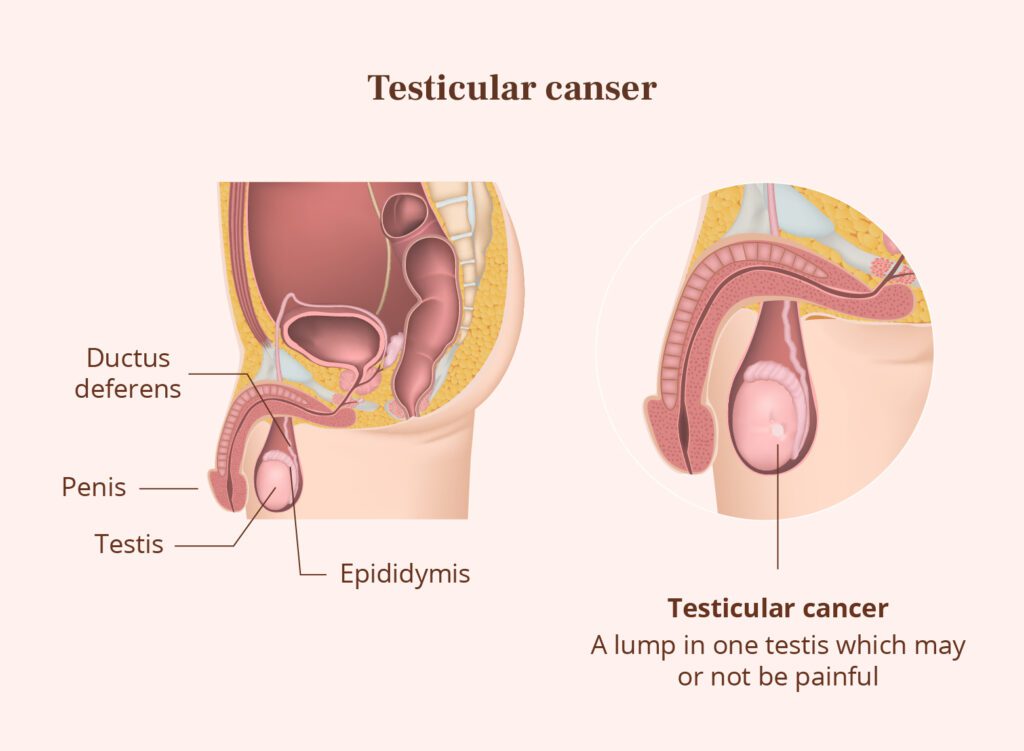
Testicular cancer typically affects younger men, with the majority of cases occurring between the ages of 15 and 40. However, it can occur at any age. Some key points to note about testicular cancer include:
Advertisements
- Risk Factors: While the exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, several factors may increase a man’s risk, including undescended testicle (cryptorchidism), family history of testicular cancer, personal history of testicular cancer, and certain genetic conditions like Klinefelter syndrome.
- Signs and Symptoms: The most common sign of testicular cancer is a painless lump or swelling in one of the testicles. Other symptoms may include a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, a dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin, enlargement or tenderness of the breasts, back pain, and fluid buildup in the scrotum.
- Diagnosis: Testicular cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests (such as ultrasound), and blood tests to measure tumor markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
- Treatment: Treatment options for testicular cancer depend on the type and stage of cancer but may include surgery (orchiectomy) to remove the affected testicle, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surveillance (active monitoring). In most cases, testicular cancer is highly treatable, with cure rates exceeding 95% for early-stage disease.
- Self-Examination: Regular testicular self-examination (TSE) can help men detect abnormalities early. It’s recommended to perform TSE monthly, ideally after a warm bath or shower when the scrotal skin is relaxed. Men should check for any changes in size, shape, or consistency of the testicles and report any concerns to a healthcare provider.
It’s essential for men to be proactive about their health and to seek medical attention promptly if they notice any changes or symptoms related to their reproductive system. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with testicular cancer.